How to Choose the Right Pilot Valve for Your Application?
Choosing the right pilot valve for your application can be challenging. Different industries and tasks demand specific features from a pilot valve. Consider the functions and environments where the valve will operate. Proper selection can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance safety.
Pilot valves come in various sizes and materials. This variation can affect performance under specific conditions. For instance, temperatures and pressures can impact a valve’s reliability. Knowing the environment will guide you to the best option. Choose a pilot valve that meets all operational needs.
Reflection is important here. Many might overlook small details or assume one size fits all. Each application is unique, and a hasty decision can lead to problems. So, take your time and evaluate your specific requirements carefully. Your choice of a pilot valve can significantly affect overall system functionality.

Understanding the Functionality of Pilot Valves in Fluid Control Systems
Pilot valves play a crucial role in fluid control systems. They regulate the flow of fluid in various applications, ensuring efficiency and precision. These valves can manage pressures, control directions, and regulate flow rates. According to industry reports, using the right pilot valve can improve system responsiveness by up to 30%. The selection of a pilot valve should consider factors like pressure ratings and flow characteristics.
Tips: Assess your system's unique requirements. Consider the fluid type and operational pressure. This can help you choose a pilot valve that meets your application needs. Ensure compatibility to avoid system failures.
Pilot valves are available in different types, such as direct-acting and solenoid-operated models. Each type offers distinct benefits depending on application demands. For example, solenoid valves are typically faster but may require more power. However, they may not perform optimally under low flow conditions. Understanding the trade-offs is essential.
Tips: Regularly review system performance. If response times decrease, it may indicate a need for a valve replacement or adjustment. Don’t overlook maintenance; a small change can have significant effects.
Identifying Key Application Requirements for Choosing a Pilot Valve
Choosing the right pilot valve is crucial for your application. Understanding your specific requirements is essential. Start by analyzing the fluid type you'll work with. Different fluids require specific valve materials. For example, corrosive fluids need appropriate materials to prevent damage.
Consider the operating pressure and temperature range too. Pilot valves need to operate effectively under these conditions. The valve should support the expected changes. It’s also important to think about flow rates. Does your application demand high flow or low flow? Match the valve specifications accordingly.
**Tips:** Always check compatibility with other components. Mismatched parts can lead to performance issues. Also, think about maintenance needs. Some valves require more upkeep than others. Efficient maintenance can save time and costs in the long run.
Evaluating Types of Pilot Valves and Their Suitable Applications
When selecting a pilot valve, understanding its type is crucial. There are several common types: solenoid, pneumatic, and electronic pilot valves. Each serves unique applications. For instance, solenoid valves excel in automated systems, while pneumatic valves are preferred in high-speed operations. According to a report from the International Society of Automation, solenoid pilot valves account for approximately 45% of the market, primarily due to their reliability in various environments.
To choose effectively, assess the specific needs of your application. For high-temperature scenarios, robust materials are essential. Some users fail to consider environmental factors, leading to premature failures. A study by the Fluid Power Society pointed out that improper selection can reduce efficiency by over 30%. This is a significant loss, particularly in industries where precision is vital.
Size and pressure ratings also matter. Many overlook their system's specifications, resulting in mismatched components. Inconsistent pressure can cause erratic operation. The valve's flow capacity should align with your application demands. For example, mismatched flow rates lead to wasted energy. A careful analysis of both the pilot valve type and the application ensures enhanced performance and longevity.
How to Choose the Right Pilot Valve for Your Application?
| Pilot Valve Type | Suitable Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solenoid Pilot Valve | Automated machinery, robotics | Quick response time, easy to automate | Requires electrical power, can overheat |
| Pneumatic Pilot Valve | Air control systems, pneumatic equipment | Suitable for high-speed applications, reliable | Sensitive to pressure fluctuations |
| Hydraulic Pilot Valve | Heavy machinery, construction equipment | Handles high pressures, durable | Can be costly, requires maintenance |
| Mechanical Pilot Valve | Manual control systems, field applications | No power required, simple design | Slower actuation, less precise |
Analyzing Technical Specifications for Optimal Pilot Valve Selection
Choosing the right pilot valve involves understanding technical specifications. Key specifications include flow rate, pressure range, and response time. A recent industry report highlighted that 75% of valve failures stem from improper selection. Therefore, analyzing these factors is critical to ensure reliable operation.
Consider flow rate. It directly impacts system efficiency. If you need 50 L/min but choose a valve rated for only 30 L/min, issues arise. Pressure range is another vital factor. A valve must handle the maximum system pressure without leakage. Research indicates that 40% of failures relate to inadequate pressure ratings.
Response time influences system dynamics. Rapid activation is crucial in high-speed applications. Delays can lead to safety hazards. However, selecting valves based solely on specifications can be misleading. Real-world conditions often vary. External factors may not align with laboratory testing. Engineers must reassess their choices continuously. Mistakes happen; learning from them leads to better decisions in pilot valve selection.
Pilot Valve Selection Criteria
This chart illustrates the key specifications to consider when selecting a pilot valve for specific applications. Each dimension is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in various operating conditions.
Considerations for Installation and Maintenance of Pilot Valves
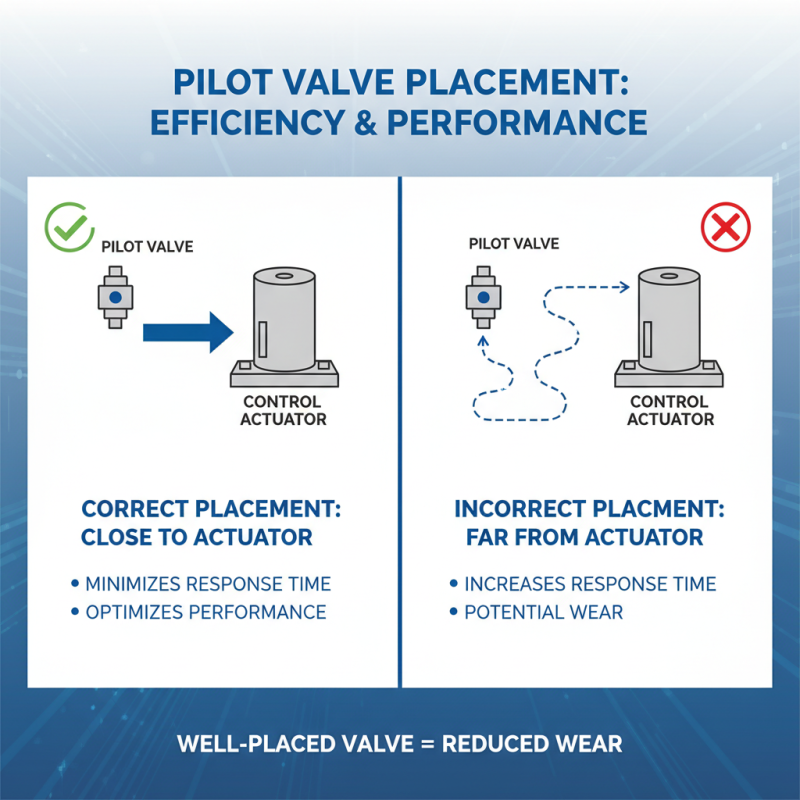
When installing pilot valves, proper placement is crucial for efficiency. Ensure they are located close to the control actuator. This minimizes response time and optimizes performance. A well-placed valve reduces potential wear over time.
Tips: Regularly check for leaks. Any signs of leakage can indicate an installation issue. Addressing leaks early can prevent larger problems later. Use proper fittings to secure connections.
Maintenance is equally important. Dust and contaminants can hinder operation. Regular cleaning is necessary, especially in dusty environments. Some might overlook this, causing unexpected failures.
Tips: Create a maintenance schedule. Consistent checks will help identify issues before they escalate. Consider the environment where the pilot valve operates. Adjust maintenance frequency based on conditions.
Related Posts
-

How to Choose the Right Lever Valve for Optimal Fluid Control in Industrial Applications
-
Top Tips for Choosing and Maintaining Your Recirculation Valve
-

Understanding the Importance of Gas Valves in Home Safety and Efficiency
-

Top 10 Tips for Choosing the Best Valve Suppliers for Your Projects
-
Top 10 Gate Valves Types and Their Best Applications for Your Projects
-
What is a Recirculation Valve and How Does It Work?
