What is a Check Valve and How Does It Work?
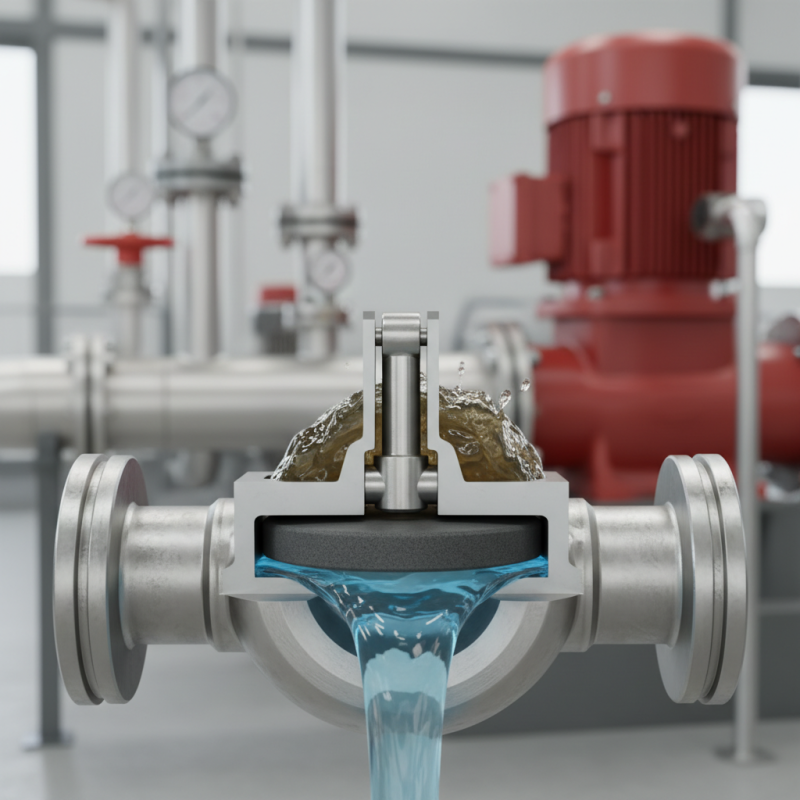
A check valve is a crucial component in various systems. It allows fluid to flow in one direction while preventing backflow. The design of a check valve is simple but effective. It typically consists of a disc or ball that moves within a housing. This mechanism is essential for maintaining pressure and ensuring efficiency in pipelines.
Understanding how a check valve works is vital for anyone involved in fluid management. For example, in a water supply system, a check valve prevents contaminated water from flowing back. This application highlights the importance of reliability in these devices. However, not all check valves are the same. Some may fail under certain pressures or temperatures, which necessitates regular inspection and maintenance.
In practical terms, check valves are found in various industries. They are used in plumbing, oil and gas, and chemical processes. Each application poses unique challenges. Over time, the effectiveness of a check valve may diminish. Users must assess their performance and understand potential risks. Awareness of these factors aids in selecting the right valve for the job.

What is a Check Valve? Definition and Key Characteristics
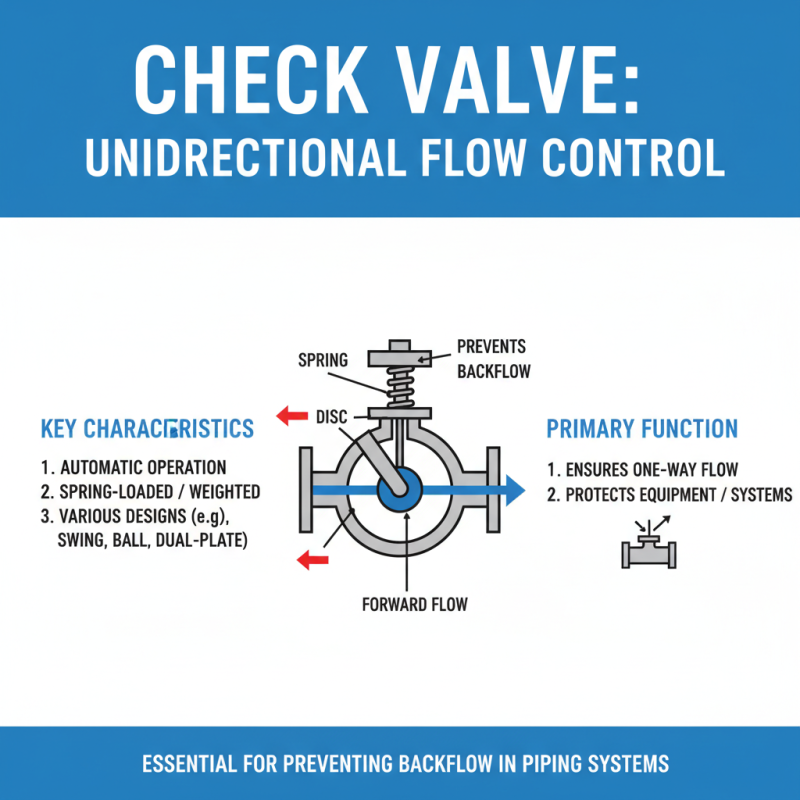
A check valve is a crucial component in various piping systems. It ensures that fluid flows in one direction while preventing backflow. This simple mechanism has key characteristics that make it valuable in numerous applications. For instance, check valves are typically spring-loaded or weighted, ensuring closure when flow reverses. Their design varies, but the function remains consistent.
Understanding different types of check valves can be beneficial. There are swing, lift, and ball types, each serving unique purposes. Swing check valves work like a hinged door. They open when fluid flows forward but close when flow reverses. On the other hand, ball check valves use a ball to seal the reverse flow. It's essential to choose the right type based on your system needs.
**Tip:** Regular maintenance is crucial for check valves. Inspect them periodically for wear and tear. This can prevent unexpected failures. Make sure you consider the environment where the valve operates. Temperature and pressure can affect performance. Not all check valves are created equal; their effectiveness varies based on their design and application.
Types of Check Valves: Overview of Common Variants and Applications
Check valves are vital components in various fluid systems. They allow flow in one direction while preventing backflow. This mechanism is crucial in many applications. Several types of check valves serve different functions and environments.
The spring-loaded check valve is one of the most common types. It uses a spring mechanism to close the valve when the flow reverses. These valves are often seen in water systems and fuel lines. Another type is the ball check valve. This variant utilizes a ball to block reverse flow, providing a simple yet effective solution. You may find it in drainage systems.
Diaphragm check valves are also noteworthy. They incorporate a flexible diaphragm that opens and closes with pressure changes. This makes them ideal for handling sludges and slurries. Each type has its strengths and weaknesses. However, careful consideration is needed when choosing one for specific applications. Choosing the wrong type might lead to inefficiencies or even system failures.
How Check Valves Function: Principles of Flow Control and Mechanism
Check valves play a crucial role in flow control systems. They allow fluid to flow in one direction while preventing backflow. This function is vital in various industries, from plumbing to manufacturing. A properly functioning check valve can save time and reduce costs. However, it isn’t foolproof.
Understanding how check valves work involves grasping the concept of pressure differences. The flow of fluid creates a pressure that opens the valve. When flow stops or reverses, a spring or gravity closes it. This mechanism seems simple, yet malfunctions can occur. Debris in the system can cause a valve to stick. Materials can become weak over time, leading to leaks.
In some cases, installation errors may also compromise performance. A check valve positioned incorrectly will not function as intended. Regular maintenance is necessary, although often overlooked. Even the best systems require attention. Awareness of these factors can enhance operational efficiency. Ultimately, acknowledging potential issues is the first step toward improvement.
What is a Check Valve and How Does It Work?
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Type of Check Valve | Swing, Lift, Ball |
| Materials Used | Stainless Steel, PVC, Brass |
| Application Areas | Water supply, Industrial fluid systems, Oil and gas |
| Pressure Rating | Up to 500 psi |
| Temperature Range | -20°C to 150°C |
| Functionality | Prevents backflow in a piping system |
| Operation Principle | Automatically opens and closes based on flow direction |
Industry Standards: Specifications and Testing for Check Valves
Check valves are essential components in various industries. They prevent reverse flow in piping systems, ensuring fluid travels in one direction. The design of check valves can differ, impacting their effectiveness and reliability. The industry has established specific standards for these devices, which guide their specifications and testing.
Standards often cover material selection, pressure ratings, and temperature limits. It’s crucial that manufacturers adhere to these specifications. Testing usually involves exposing the valves to extreme conditions. Each valve undergoes rigorous checks for leaks and functionality. Despite these measures, inconsistencies may arise. Some valves may fail to operate as expected under certain conditions. This can lead to significant issues in a system.
Not all check valves are created equal. Some may not perform well in corrosive environments. Others might struggle with high-pressure applications. It's vital to choose the right type for the task. Regular inspections and adherence to industry standards can help mitigate risks. This is an ongoing challenge many face, and improvements are always needed.
Applications in Various Industries: Check Valves in Real-World Systems
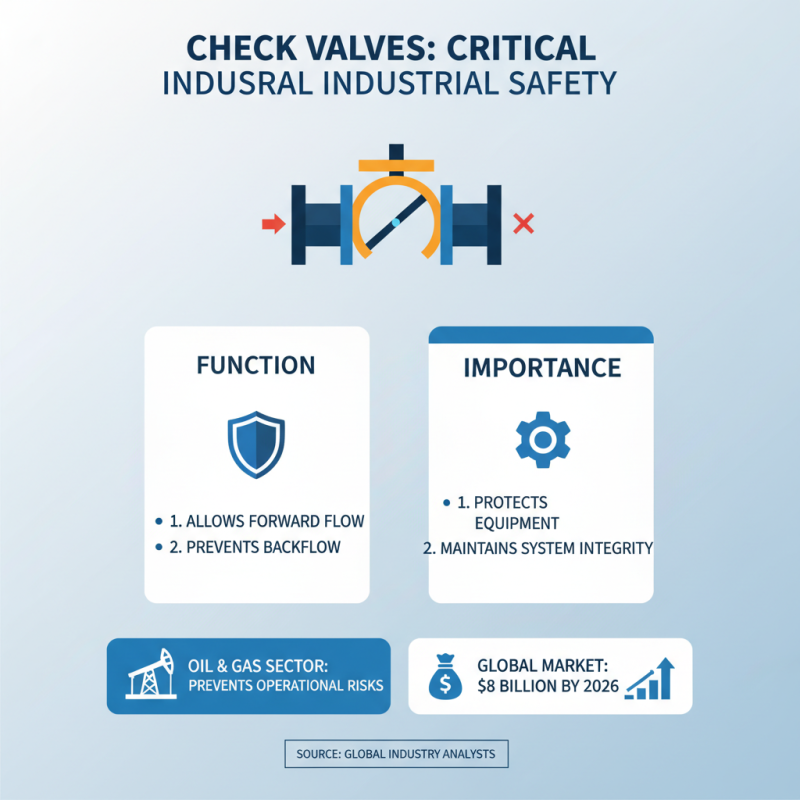
Check valves play a critical role in numerous industries. They are designed to allow fluid flow in one direction while preventing backflow. This simple mechanism protects equipment and maintains system integrity. For example, in the oil and gas sector, backflow can lead to significant operational risks and financial losses. A report by the Global Industry Analysts suggests that the check valve market will reach $8 billion by 2026, driven by its safety features.
In water treatment facilities, check valves are essential. They ensure that treated water does not flow back into the supply. This is vital for preventing contamination. According to recent studies, poorly maintained check valves can lead to over 15% inefficiency in water distribution systems. Regular inspections can mitigate such issues, yet many facilities struggle to keep up.
Furthermore, in HVAC systems, check valves maintain pressure and optimize energy usage. A failing check valve can cause leaks and increase energy costs. The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers indicates that proper valve selection can improve system efficiency by up to 30%. However, selecting the right valve isn't always straightforward. Engineers often encounter challenges in choosing materials suitable for their specific environment. This complexity highlights the need for ongoing education in valve technology for all industries.
Related Posts
-

Exploring the Best Check Valve Options for 2026 Top Industry Trends?
-

Understanding the Importance of Shut Off Valves in Home Plumbing Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
-
Understanding the Role of Combination Valves in Modern Plumbing Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
-

Top 10 Valve Home Innovations to Watch in 2025
-

2025 How to Choose the Best Valve Products for Your Industry Needs
-
What is a Valve Home and How Does It Work?
